As our industries grow, the need to optimize our production cycles is inevitable. From raw materials to tooling, we are aiming at cost efficiency and quality.
Focusing on the plastic industry, we can see developments in machinery and tooling. Over the years, we have seen plastic production leap huge strides. Take a look at plastic injection molding. The art dates back to the 19th century. John and Isaiah Hyatt are the minds behind the concept of injection molding.
From then we have seen developments on the idea to the point of integrating automation in the cycle.
We are now using polycarbonates as raw materials in injection molding. Polycarbonate injection molding is becoming popular due to the many benefits it holds.
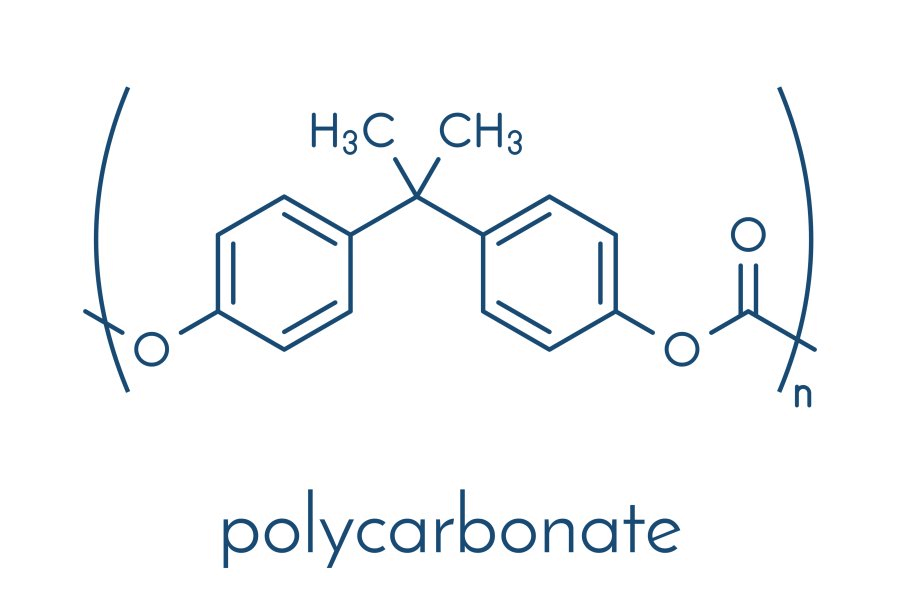
What are Polycarbonates?
Polycarbonates are a group of amorphous thermoplastics with carbonate groups in their structure. These plastics exhibit high levels of toughness and other unique properties. You can mold them with a lot of ease. These properties give them many applications in the plastic industries.
Characteristics and Properties of Polycarbonates
Bundled with a unique set of chemical and physical properties, PCs are better than glass, PMMA, and PE.
Toughness and high impact strength.
Polycarbonates exhibit high levels of strength and resistance to impact and fracture. With a density of 1.2-1.22g/㎤ and toughness retention with temperatures of up to 140℃ PCs are unbreakable.
Transmittance
Polycarbonates are clear plastics that allow 90% of light to pass through. This feature makes them ideal for making parts in some industries like automotive. You can also get customized polycarbonate sheets depending on your color preferences.
Lightweight.
Polycarbonates are six times lighter than standard glass. This makes installation much easier and increases efficiency. You will also save on transport costs.
Protection from harmful UV rays
Polycarbonates come with the bonus of protecting us from UV light. You can rest assured of 100% safety when dealing with UV light.
Optical Nature
The Amorphous nature of polycarbonates makes them ideal for optical use. Clear polycarbonates have a refractive index of 1.584
Chemical and heat resistance
PCs show high levels of resistance to diluted acids and alcohol. It is worth noting that PCs can react with dilute alkali. You should not clean parts made of PCs with alkaline soaps. Polycarbonates show stability up to temperatures of 135℃
Polycarbonate injection molding process
Parts produced by this means exhibit a wide range of geometric complexity. You will also have outstanding part-part repeatability. This implies that the process is ideal for the long-run production of similar parts. Polycarbonate injection molding utilizes rapid heating and cooling to give parts with:
- Superior impact strength
- High rigidity
- Crystal clear transparency
- Low deformation
- Low moisture absorption
Polycarbonate injection molding Applications
PCs are versatile and easy to work with. The unique set of characteristics give it dozens of applications. Quality surfaces give high-end aesthetic value. Applications include:
- Automotive components; include headlight lenses, fenders, grilles, bumpers, and floor rails.
- Eyeglass lenses. This is because of their optical nature
- Medical tubing
- Electrical insulators
- Lighting fixtures
Polycarbonate injection molding techniques
When it comes to Polycarbonate injection molding we have a list of techniques we can deploy in the cycle.
Optical molding polycarbonate
This involves the production of high-precision parts that don’t need polishing and grinding. It is also known as ultra-precision thermal pressing. It has gained popularity due to the need for sophisticated light handling components.
Thin wall polycarbonate molding
This is a specialized process that focuses on producing mass parts
You will need machines and tools with high levels of stress and pressure tolerance. Parts and components produced are thin and light. The thickness is reliant on the size of parts you aim to produce. The cycle is shorter hence reducing lead time and cost per part.
Water assist injection molding
This process uses fluids under high pressure to produce hollow plastic parts. Injecting water at high pressure ensures the evenness of walls in plastic parts. You will also get parts with quality surfaces. The advantages of this process are;
- Lower tool cost
- Part consolidation
- Direct cooling
- Smooth internal part surfaces
Two-component Polycarbonate injection molding
At this juncture, two or more thermoplastic resins produce a part. You will be injecting a resin while altering the cavity hole as you inject the second resin. It work with materials of different properties.
It is worth noting that you can meet two-component molding through several ways;
Mixed materials
Under this method, you will be feeding resins at the same time and mix them as heating continues. This method is ideal for Aesthetic purposes.
Bi-injection
Injection of resins occurs at different points in the cycle and different hollows. The materials begin to harden before they meet in the mold cavity.
Co-injection
Co-injection involves the injection of two full resin shots one after the other. It is ideal for the manufacture of parts with soft rubber around a harder plastic part.
Overmolding
This method deploys an add-on operation. You will create a component first and allow it to harden and a second part over it. This method gives you room for flexibility with materials and construction.
Sequential molding (Multi-shot molding)
What you are aiming for in this cycle is the layering effect on your parts. You will achieve this by injecting partial shots of resins in a sequence. For clarity, note that materials do not mix, they stack up into a finished component.
Compression molding
This method involves low stress during polycarbonate injection molding. Your results will be thick-walled components and excellent contour accuracy. You also manage defects like sink marks. Upon injection, we clamp the mold with compression. This will allow uniform distribution of the resin. It is ideal for components that bear adornments and insertions. You can use it with components that need low stress and a downstream heat cycle.
Structural foam molding
We use this method for large parts. It involves the addition of a blowing agent and extensive modification of the cycle. This is all in a bid to achieve a sandwich-like construction.
Advantages of this method are;
- Low initial investment
- Superb strength to weight ratio
Polycarbonate injection molding parameters
To meet our desired results there are parameters we should put into consideration. These are;
Injection molding temperature
In any injection molding process, temperatures play a role in the quality of the end product. You need to determine the ideal temperature for the whole of the process. Here are some factors you should consider when determining temperature;
- The polycarbonate material
- Mold size
- Melting point
- Coolant type
- Heating and cooling channels
We have several structures under temperature that determine the quality of parts. They are;
The temperature of the screw barrel
The screw barrel applies pressure to the heated resin forcing it into the cavity mold to form parts. As you can see, you need to regulate the temperature of the screw barrel if you are to achieve your desired results. Luckily most injection molding machines have temperature control units for screw barrels. This allows you to set an optimal temperature throughout the process.
Polycarbonate melt temperature
This refers to the exact temperature of the resin, the instant it enters the mold. This plays a vital role in the effectiveness of the process and the quality of finished parts.
The settings on this depend on factors like;
- Shot size
- Backpressure
- Screw rotational speed
- Molding cycle
Polycarbonate injection molding temperature
It implies the range of temperature at which a polycarbonate melts.
High temperatures increase the flow rate but bring about defects like;
- Flash
- Shrinkage
- Internal stress
Extreme temperatures will degrade your resin.
Factors to consider are;
- Injection pressure
- Backpressure. It is the pressure exerted by the resin during the return action of the screw barrel. You should keep it as low as possible. Back Pressure ensures uniformity in temperature and viscosity.
Recovery rate
Recovery rate is the volume of resin released from a nozzle per unit of time at 50% injection capacity. A high recovery rate will shorten your cycle time. It eliminates the use of nozzle shutoff valves.
Moisture control
PC plastics are prone to hydrolysis, weight reduction, strength reduction, and bond breaking. This can happen on exposure to even low levels of moisture. The moisture content of resins should be lower than 0.02% You should dry your resins in a hot air drier for 3-5 hours at 120. You can also use a dehumidifier set at -30 degrees Celsius.
Polycarbonate Injection molding defects
Injection molding is one of the best plastic production methods. We will now look at the problem you are likely to encounter and how to fix them.
Flow lines
Flow lines appear like off-tone patterns on the surface of your finished parts. Flow lines are the results of slow injection rate and disparities in flow rate. The heated resin solidifies at different stages. To fix flow lines, you need to increase your injection speed and pressure. You can also raise temperatures to ensure uniform and slow cooling.
Flash
Flash occurs when the resin attempts to escape from the mold. You may be having loose clamps or too much pressure. It will appear like excess structures which you can shave off. You should increase clamp pressure and cut cleaning and maintenance. You should additionally revise your mold temperature and injection speed.
Sink marks
They appear as depressions on the thicker areas of parts produced. It is a result of bad cooling techniques and time. You can reduce the mold temperature and increase holding time.
Weld lines
Weld lines are the sutures you notice where two parts of the resin meet in the mold. It is as a result of the rein flowing from more than one source. You should;
- Increase mold temperature
- Increase injection speed
- Use a less viscous resin
- Use only one flow source
Jetting
These are wavy folds on the surface of parts. It is a result of low melt temperature, low injection speed, and high viscosity.
You should be careful with jetting because the above reasons are concurrent. You should ensure that there is ample contact between the walls of your mold and the resin.
Warping
Warping will make your parts appear bent, twisted, or uneven
It is a result of non-uniform cooling or stress on different cooling stages. To fix warping, you should not rush cooling. Ensure that the wall thickness in the mold is uniform.
Burn marks
Burn marks appear like scorched spots on the surface of parts. Burn marks are the results of excess heat in the mold or overheating trapped air. You should reduce your mold temperature and remove trapped air in your mold.
Conclusion
I believe that you have grasped the concept of polycarbonate injection molding. The beauty of learning about a process is you get to appreciate its dynamics. Polycarbonate injection molding has various applications ranging from automotive to medical equipment. Using PCs will give you quality parts with high impact strength.
If you still have any questions feel free to leave a comment or contact us.